Augmenting Efficacy of Topical 5-FU for Actinic Keratoses and Skin Cancer
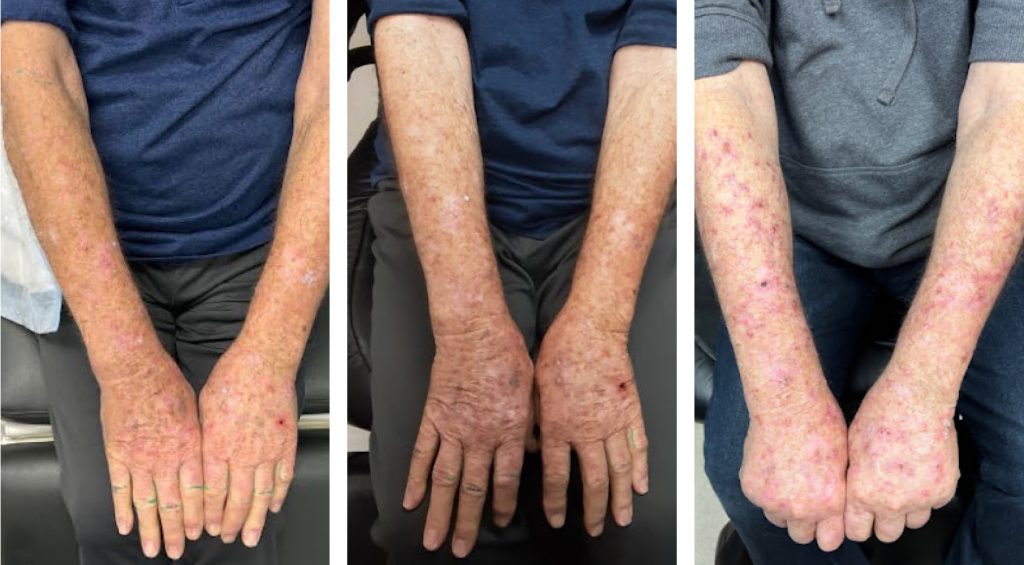
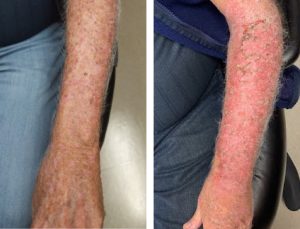
Diffuse actinic sun damage can present a challenge for both patients and providers. First line treatment options include topical 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) cream or photodynamic therapy (PDT). Topical 5-FU cream is applied to the affected area for 2-3 weeks creating inflammation, redness, and crusting as the body eliminates the actinic damage. Alternatively, topical levulan is applied to the affected area followed by the 17 minute blue light exposure of PDT. The blue light activates the levulan causing a chemical reaction that treats the actinic damage. Similar to a 5-FU reaction, in PDT the patient can expect redness, peeling, and crusting.
However, sometimes a patient has little to no response after 5-FU or PDT.
To augment the 5-FU reaction, the cream can be mixed with other products such as calcipotriene. Calcipotriene is a vitamin D analogue that works synergistically with 5-FU. It is commonly used to treat the thick plaques of psoriasis. Similarly, it works to help reduce the thick, hypertrophic AKs when 5-FU alone is not effective. Calcipotriene 0.005% cream can be mixed 50:50 with 5-fluorouracil 5% cream and applied to the affected area for a few weeks. For convenience, a combination cream can be formulated at a specialty pharmacy so the patient only has one cream to directly apply. The cost can range around $50-120 for the combination cream.
Alternatively, a thick layer of 5-FU can be applied and then covered with Saran wrap or a zinc oxide wrap for occlusion. Zinc oxide is commonly used to prevent diaper rash in infants because it protects the skin from moisture and irritation. Similarly, the zinc oxide wrap improves tolerance of the treatment. The wrap also provides occlusion for better absorption. In outside studies, patients wore a zinc oxide wrap for a week at a time which was well tolerated due to the soothing effect of zinc oxide and resulted in improvement in AKs. Saran wrap can be applied overnight to augment 5-FU action.