Near-Infrared Laser Lymphangiography Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy for Melanoma
HISTORY
A 61-year-old male presents for 1.5 cm malignant melanoma of left posterior shoulder invading to at least 1.2 mm (Clark’s Level IV) on a shave biopsy. Left shoulder melanoma was excised, and a left axillary sentinel lymph node was biopsied. Small focus of residual melanoma was found in the primary site, but none in the lymph node. DecisionDx melanoma gene expression profile demonstrated the melanoma as Class 1A (lowest risk of recurrence), and genetic testing was positive for BRAF mutation on DecisionDX-CMSeq test.
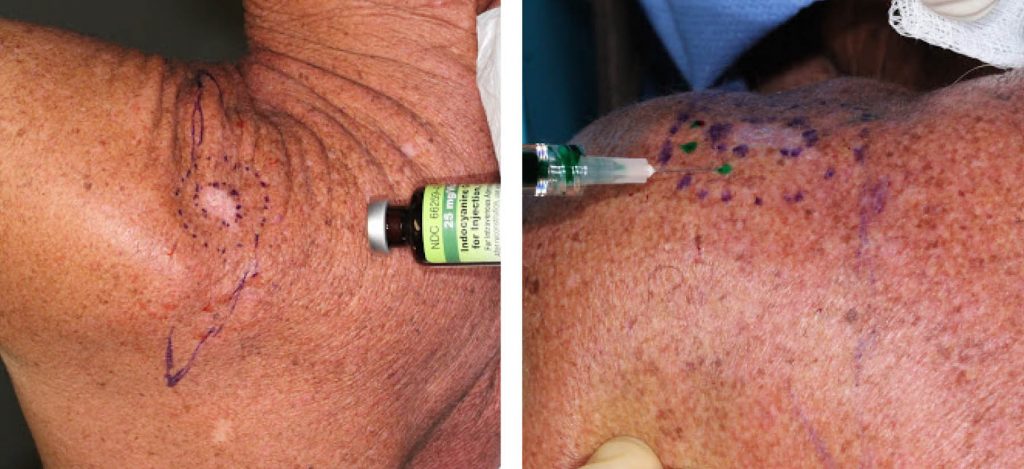
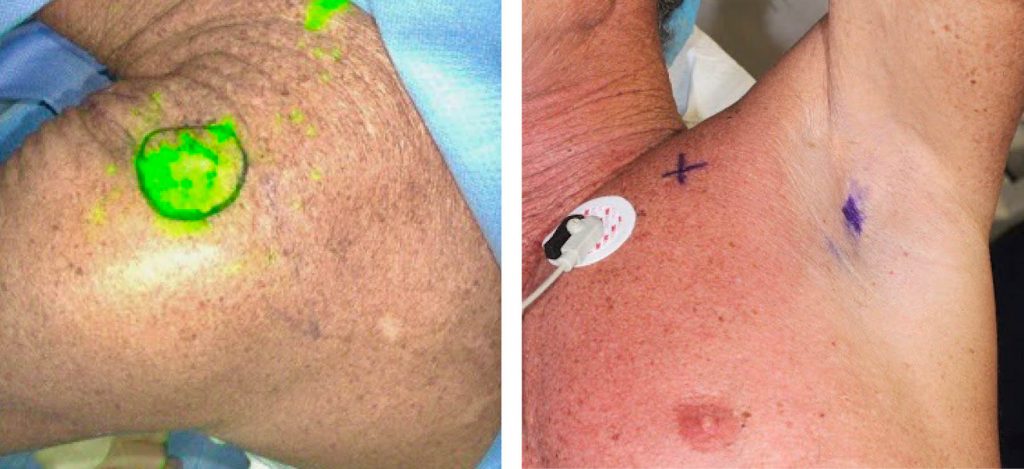
Right: Axilla with location of sentinel lymph node identified with a gamma probe
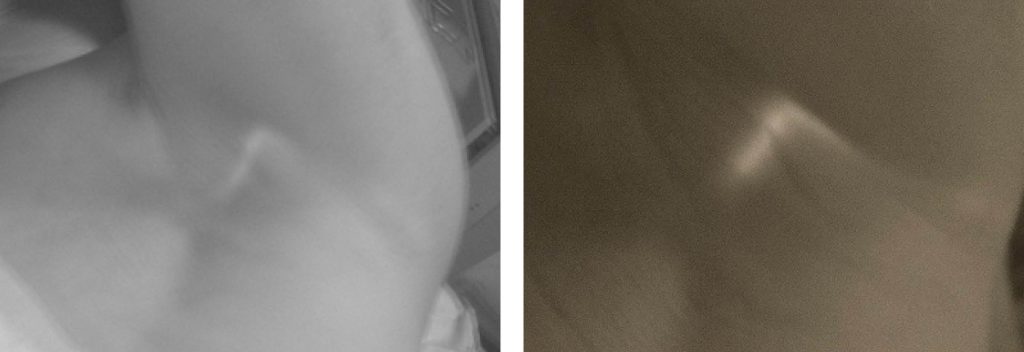
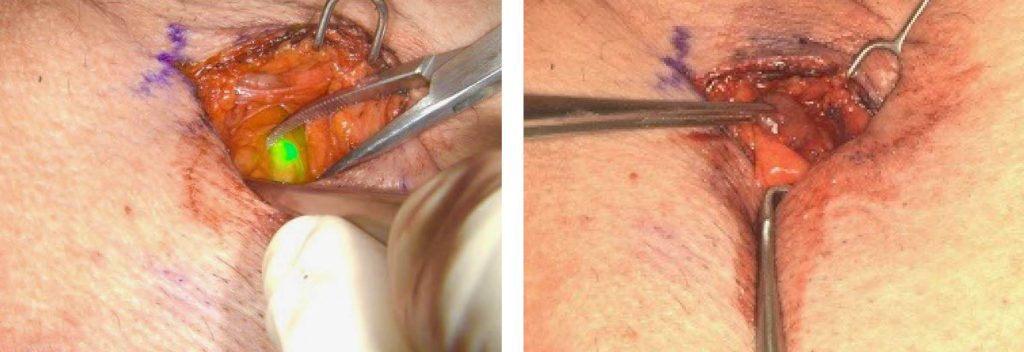
Right: Same lymph node visualized with a naked eye
DISCUSSION
Sentinel lymph node biopsy can be a minimally-invasive surgical procedure but not always. The radiotracer guided identification with a handheld gamma probe can easily identify the lymph node. Auditory feedback form this “Geiger counter” suggests proximity to the radiotracer-containing lymph node. However, in some cases the deeper lymph nodes are harder to find and require a greater amount of surgical dissection. Methylene blue dye is an adjunct used to help with direct visual identification. Like the radiotracer, it is injected in the skin around the primary cancer site and is then visualized in the sentinel lymph node. It serves as confirmatory evidence of the sentinel lymph node, while the gamma probe is the primary detector of it.
Near-infrared laser (NIL) lymphangiography with indocyanine green (ICG) fills the technological void between gamma probe detection and direct visual identification of the methylene blue dye. It visualizes the ICG containing lymph node 5 – 10 mm through surrounding tissue. It has been shown to increase the precision of lymph node detection. This spectrum of technologies is analogous to the self-driving car obstacle detection. There are the proximity ultrasonic detectors for up to 8 m, cameras for mid distance, and radars for far distance. Similarly, methylene blue is the proximity detector, ICG guided NIL lymphangiography is the mid distance camera, while the gamma probe is the far distance radar.
Combining existing gamma probe technology, methylene blue visualization, with the ICG guided near infrared lymphangiography shortens the operative time, limits the surgical dissection, and increases the precision of lymph node detection.
