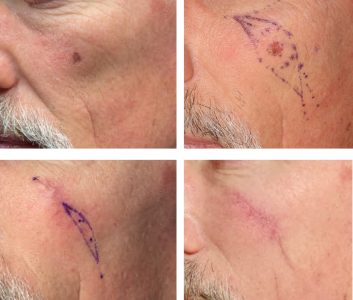
ABOUT ATYPICAL FIBROXANTHOMA (AFX)
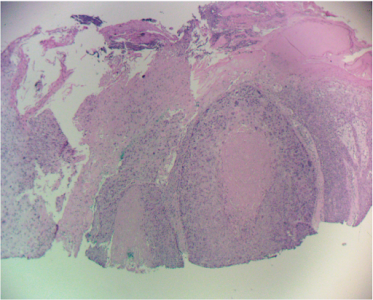
Atypical Fibroxanthoma of the skin (AFX) is an uncommon tumor of sun-exposed areas of elderly white men, most commonly on the scalp and ears. This fibro-histiocytic spindle cell neoplasm has a potential to metastasize and behave aggressively. Diagnosis is made by immunohistochemistry. AFX is histologically indistinguishable from malignant fibrous histiocytoma (MFH); therefore, its clinical presentation must be used as a guide to its true behavior. Superficial lesions behave in a benign fashion and are called AFX, while lesions with subcutaneous extent or larger size have a higher tendency for lymph node and distant metastases and are called MFH. A corollary to the above also holds true. When regional metastases are found, the lesion is classified as MFH. Local recurrence can also be used to reclassify an AFX as a MFH. However, if the lesion “recurs” simply due to incomplete excision, its diagnosis should not be changed.
AFX has also been described as a superficial manifestation of MFH. Ronald Barr, M.D., (Dermatopathology) also believes that, comparing AFX to a superficial leimyosarcoma of the skin (SCARS Tumor Conference, 9/1/2011). The latter arises in piloerector muscles and behaves very differently than a deeper arising leiomyosarcoma that has a worse prognosis. As such, leimyosarcoma parallels behavior of AFX / MFH. A recent Mayo Clinic review of AFX found that 3.4% of these lesions transform into MFH or develop metastases within 2 years of treatment.
TREATMENT
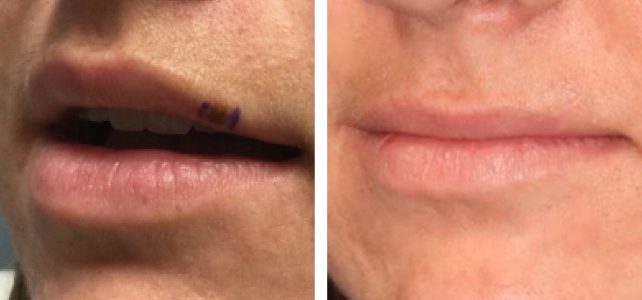
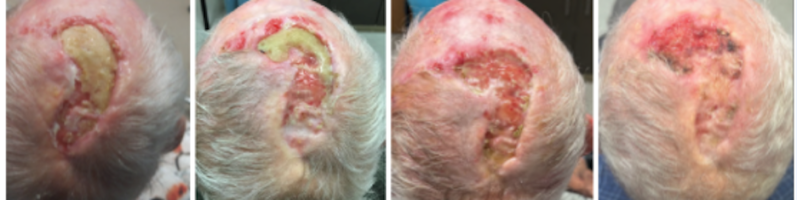
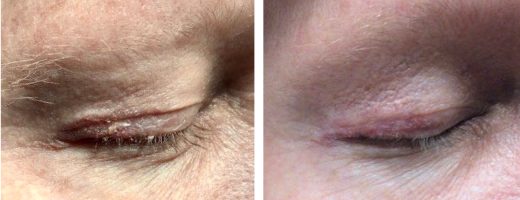
Treatment of atypical fibroxanthoma of the skin (AFX) includes curettage and dessication (C&D), wide local excision (WLE), and Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS). Although all three are within the standard of care, the same Mayo clinic review found significant differences in recurrence rates. With Mohs micrographic surgery the recurrence was 0%, and with wide local excision it was 8.7%. WLE with 2 cm margins was recommended to ensure 96.6% clearance. However, MMS achieved cure with more tissue sparing. A two-year follow-up is recommended after resection to monitor for regional metastases or recurrences.
Treatment of lesions that behave as MFH (metastatic and recurrent) is surgical resection followed by radiation therapy. The differential diagnosis for spindle cell neoplasm, such as AFX, includes spindle cell squamous cell carcinoma, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, and desmoplastic melanomas.
Related Articles
Management of Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in Bowen’s Disease
Treatment Considerations for Melanoma In-Situ
Management of Non-Healing Lesion
Managing Eyelid Skin Cancer
Managing Lentigo Maligna Melanoma
A Modern Test for Melanoma
STAY UP TO DATE
Receive research updates, inspiring stories, healthy living tips and more.
CME ACCREDITED SKIN CANCER CONFERENCE
Earn your CME credits at the SCARS Foundation Monthly Skin Cancer Conference
FOLLOW US
ELEVATING THE STANDARDS OF SKIN CANCER MANAGEMENT.