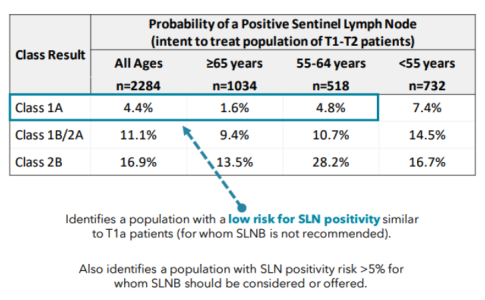
About Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy (SLNB) is a surgical procedure used to determine the extent of involvement or stage of certain types of cancers such as melanoma, breast cancer, squamous cell carcinoma, and basosquamous cell carcinoma. The test determines if cancerous cells have metastasized from the original, primary tumor site into the lymph nodes. Thus, SLNB determines the prognosis and guides the treatment.
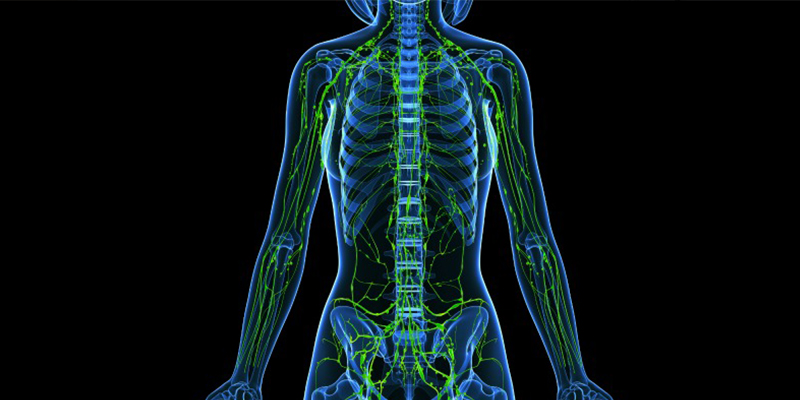
The lymphatic system carries lymphatic fluid to the central chest, and is interrupted by multiple filters along the way - the lymph nodes. The lymphatic system provides a pathway for cancer cells to travel and spread. The first node to receive lymphatic drainage from a tumor is called the sentinel lymph node. Cancer cells may appear in the sentinel node before spreading to other lymph nodes.
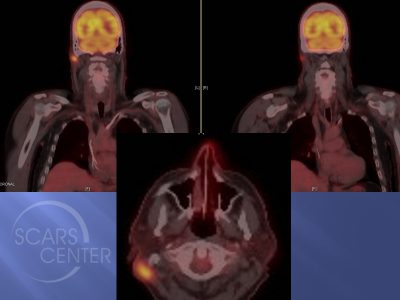
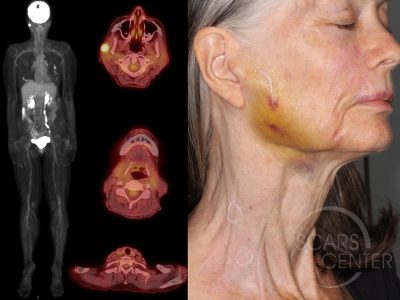
SLNB is done prior to removal of the main tumor. It is a two step process which involves first identifying the sentinel lymph node followed by its removal and microscopic evaluation. The process begins at a Nuclear Medicine department of a radiology facility. The radiologist injects a harmless radioactive substance near the tumor. After 15 – 60 minutes, the area is scanned with radiation detectors to show where the substance has traveled within the lymphatic system. The images of this are then taken by the patient to their scheduled biopsy at a surgical facility.
In the operating room, the surgeon will use the Nuclear Medicine images as well as a special radiation-detecting probe (Gamma probe) to identify the greatest concentration of the radioactive tracer. Like cancer cells, the radioactive tracer will get temporarily trapped in a lymph node--a filter of the lymphatic system. The first lymph node to show the radioactive tracer is the sentinel lymph node. Frequently, the surgeon also injects a dye called methylene blue into the tumor prior to surgery. 15-30 minutes later, when the lymph node is being identified with the gamma probe, the dye can be seen staining the sentinel lymph node. This helps confirm that this is indeed the first lymphatic filter for the cancer.
Once the the surgeon identifies the lymph node, it is removed. The lymph node is sent to a pathologist for specialized testing to identify cancer cells. Identification of cancer cells within the sentinel lymph node results in more aggressive treatment such as radiation therapy, extensive lymph node removal, or even chemotherapy.
Related Articles
A Modern Test for Melanoma
Multiple Cutaneous Carcinomas in Organ Transplant Recipients
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy for Cutaneous SCC
Melanoma within recurrent MIS
Scalp SCC Metastasis to Neck
RECURRENT MELANOMA
STAY UP TO DATE
Receive research updates, inspiring stories, healthy living tips and more.
CME ACCREDITED SKIN CANCER CONFERENCE
Earn your CME credits at the SCARS Foundation Monthly Skin Cancer Conference
FOLLOW US
ELEVATING THE STANDARDS OF SKIN CANCER MANAGEMENT.